Frequently Asked Questions¶
General Questions¶
What is Substation?¶
Substation is an terminal user interface (TUI) for OpenStack cloud management. It provides a powerful, keyboard-driven interface that allows operators to manage OpenStack resources efficiently from the terminal, with features like batch operations, real-time monitoring, and intelligent caching designed to reduce API calls by up to 60-80%.
Why use Substation instead of Skyline/Horizon or the OpenStack CLI Directly?¶
Substation offers several advantages:
- Terminal-native: Designed specifically for terminal workflows, not adapted from web
- Performance: Designed for up to 60-80% reduction in API calls through intelligent caching
- Batch operations: Process hundreds of resources simultaneously
- Real-time updates: Live status updates without manual refresh
- Keyboard-driven: Maximum efficiency for power users
What OpenStack versions are supported?¶
Substation supports OpenStack Queens and later. We recommend using Caracal (2024.1) or newer for the best experience. The latest LTS versions are extensively tested.
Is Substation open source?¶
Yes, Substation is open-source software licensed under the MIT License. You can contribute, fork, or modify it according to your needs.
Installation & Setup¶
What are the system requirements?¶
- Operating System: macOS 13+ or Linux
- Swift: Version 6.1 or later
- Terminal: Any terminal emulator with ncurses support
- Memory: Minimum 256MB RAM (512MB recommended)
- Network: Access to OpenStack API endpoints
Where should I put my clouds.yaml file?¶
Substation looks for clouds.yaml in these locations (in order):
./clouds.yaml(current directory)~/.config/openstack/clouds.yaml(recommended)/etc/openstack/clouds.yaml
Can I use environment variables instead of clouds.yaml?¶
No, Substation does not support standard OpenStack environment variables:
Usage Questions¶
How do I connect to multiple clouds?¶
Define multiple clouds in your clouds.yaml:
Then switch between them:
How do I search for resources?¶
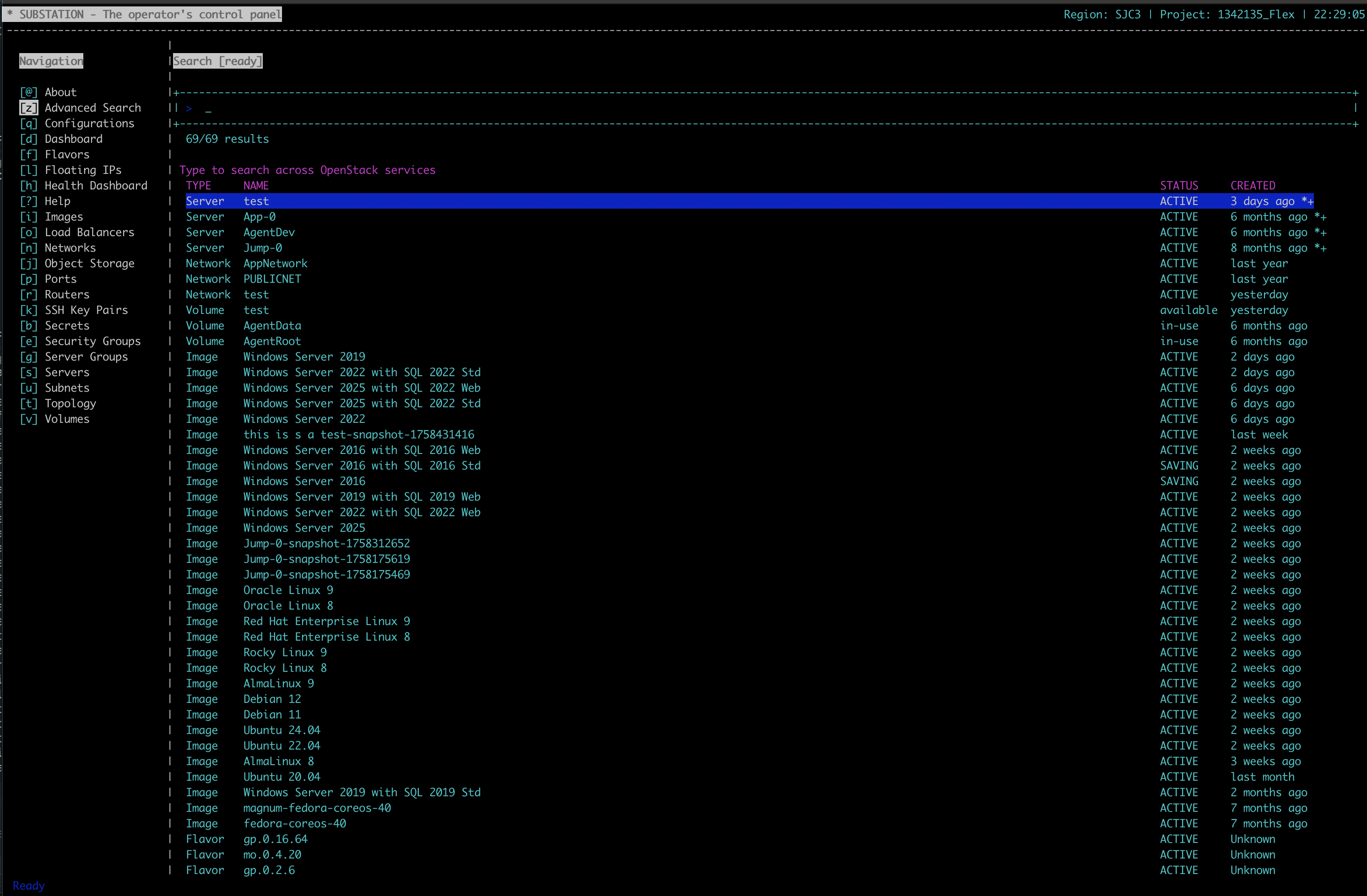
Substation provides two search methods:
- Quick search (/): Type to filter visible resources instantly
- Advanced search (z): Complex queries across all services
For detailed information about search capabilities, see the Search Engine Guide.
Performance Questions¶
Why is everything slow? (The Most Common Question)¶
Short Answer: It's probably your OpenStack API, not Substation.
How to Verify:
# Enable wiretap mode to see actual API response times
substation --cloud mycloud --wiretap
# In another terminal
tail -f ~/substation.log | grep "ms)"
What you'll see:
CACHE HIT: servers (L1, 0.8ms) <- Substation is fast
GET /servers/detail <- 200 (2134ms) <- OpenStack is slow
Interpretation:
- Cache HIT < 20ms: Substation working perfectly
- API calls < 2 seconds: Normal OpenStack performance
- API calls 2-5 seconds: OpenStack under load (common)
- API calls > 5 seconds: OpenStack cluster has problems
Solution: If your OpenStack API is slow, Substation can't fix that. But caching helps minimize the pain.
How is Substation designed to achieve up to 60-80% API call reduction?¶
Through a multi-level caching architecture (MemoryKit). For detailed information about the caching system, see the Caching System Guide.
Quick Overview (Design Targets):
- L1 Cache (Memory): Target < 1ms retrieval, target 80% hit rate
- L2 Cache (Larger Memory): Target ~5ms retrieval, target 15% hit rate
Note: Actual cache hit rates will vary based on your usage patterns and resource churn rate. 3. L3 Cache (Disk): ~20ms retrieval, 3% hit rate 4. API Call: 2+ seconds, 2% miss rate
See Performance Tuning for cache configuration details.
Why is Substation using so much memory?¶
Expected Memory Usage:
- Base application: ~200MB
- Cache for 10,000 resources: ~100MB additional
- Total typical: 200-400MB
For large deployments:
- 50,000 resources: ~500MB
- 100,000 resources: ~800MB
This is normal. If memory is constrained:
- Use
/to filter views (reduces visible resources) - Use project-scoped credentials (reduces total resources)
- Use
:cache-purge<Enter>(or:cc<Enter>) to manually purge cache
Automatic Eviction: Substation auto-evicts cache at 85% memory threshold to prevent OOM.
Why is my cache hit rate low?¶
Press h in Substation to view the Health Dashboard and check cache hit rate.
Target: 80%+
Common causes of low hit rate:
- You're constantly pressing 'c' (cache purge) - Don't do that unless data is stale
- Switching views rapidly - Each view may trigger cache refresh
- Large dataset (50K+ resources) - First-time cache warming takes longer
- Memory pressure - System evicting cache due to low RAM
Solution: Let the cache warm up. After initial load, hit rate should stabilize at 80%+.
How can I improve response times?¶
1. Let the cache work:
- Don't constantly press
c(cache purge) - Give cache time to warm up on first load
- Expect first view to be slow, subsequent views fast
2. If OpenStack API is slow (> 2s per call):
- Talk to your OpenStack administrator
- Consider API performance tuning
- Check if OpenStack cluster is under load
3. For large datasets (50K+ resources):
- Use project-scoped credentials (reduce visible resources)
- Filter views with
/(local filtering, instant) - Be patient on first load (cache warming)
Troubleshooting Questions¶
Why can't I connect to OpenStack?¶
Common causes:
- Wrong auth URL - Must include
/v3:
# Correct
auth_url: https://keystone.example.com:5000/v3 [x]
# Wrong
auth_url: https://keystone.example.com:5000 [ ]
- Missing domain fields - Required even for default domain:
auth:
username: operator
password: secret
project_name: myproject
project_domain_name: default # Required!
user_domain_name: default # Required!
- Network issues - Check connectivity:
- SSL certificate problems - For testing only:
Why do I see "Endpoint not found" errors?¶
Meaning: Service not in Keystone catalog.
Common causes:
- Service not installed (e.g., Octavia not available in your cloud)
- Wrong region specified
- Service disabled
Solution:
# List available services
openstack catalog list
# Check specific service in your region
openstack endpoint list --service nova --region RegionOne
If the service is missing, it's not available in your OpenStack deployment. Substation will skip it gracefully.
Why is my data stale or wrong?¶
Cause: Cache contains old data.
Solution: Use :cache-purge<Enter> (or :cc<Enter>) to purge ALL caches
This clears L1, L2, and L3 caches. Next operations will be slower while cache rebuilds, but data will be fresh.
When to use:
- Just launched 50 servers, not showing up
- Deleted resources still visible
- Resource states incorrect (shows ACTIVE, actually ERROR)
- After major cluster changes
Note: Don't spam c. Let the cache work for you. Only purge when data is actually wrong.
Why did my authentication fail with "401 Unauthorized"?¶
Cause: Token expired or invalid credentials.
Substation automatically refreshes tokens, but if you see this:
Solutions:
- Verify credentials work with OpenStack CLI:
- Check domain configuration in clouds.yaml - Both domains required:
- Try application credentials instead (more reliable):
Should I use project_id or project_name in clouds.yaml?¶
Use project_id for a more explicit configuration. IDs don't change while names can be modified by admins:
clouds:
mycloud:
auth:
auth_url: https://keystone.example.com:5000/v3
username: operator
password: secret
project_id: a1b2c3d4e5f6g7h8i9j0 # Preferred
user_domain_id: default
project_domain_id: default
Benefits:
- IDs never change (names can be modified by admins)
- Faster authentication (no name-to-ID lookups)
Find your project ID:
For more details, see ID-based Authentication.
Why do I get "403 Forbidden" errors?¶
Meaning: You're authenticated, but don't have permission.
Common causes:
- Insufficient role - Need admin, member, or reader role
- Wrong project scope - Viewing resources in different project
- Quota exhausted - Can't create more resources
Solutions:
# Check your role assignments
openstack role assignment list --user myuser --project myproject
# Check quotas
openstack quota show myproject
# Request admin to adjust roles or quotas
Why are colors not displaying correctly?¶
Check your terminal configuration:
Solution:
How do I debug connection issues?¶
Enable wiretap mode for detailed API logging:
# Enable detailed logging
substation --cloud mycloud --wiretap
# View logs in real-time
tail -f ~/substation.log
Wiretap shows:
- All HTTP requests (method, URL, headers)
- All HTTP responses (status, body, timing)
- Authentication token exchange
- Service catalog discovery
- Cache hit/miss statistics
What do I do if the display is corrupted?¶
Quick fix:
Full terminal reset:
Why does search take so long?¶
Advanced search (z) searches across 6 services in parallel.
Expected performance:
- With cache: < 500ms
- Without cache (first search): Up to 5 seconds
If search takes > 5 seconds:
- Your OpenStack APIs are slow
- Enable wiretap to see which service is slow:
Note: Search has a 5-second timeout. If a service doesn't respond in time, you'll get partial results (other services still return data).
Can I use Substation with multiple OpenStack clouds?¶
Yes! Define multiple clouds in clouds.yaml:
clouds:
production:
auth:
auth_url: https://prod.example.com:5000/v3
username: prod-operator
password: prod-password
project_name: production-ops
project_domain_name: default
user_domain_name: default
region_name: RegionOne
staging:
auth:
auth_url: https://staging.example.com:5000/v3
username: staging-operator
password: staging-password
project_name: staging-ops
project_domain_name: default
user_domain_name: default
region_name: RegionOne
Switch between them:
Technical Questions¶
What programming language is Substation written in?¶
Swift 6.1 with strict concurrency enforcement.
Why Swift?
- Actor-based concurrency (no race conditions by design)
- Compile-time thread safety guarantees
- Memory safety without garbage collection
- Cross-platform (macOS and Linux)
- Minimal external dependencies, we know our supply chain.
Code Statistics:
- OSClient (OpenStack API library)
- MemoryKit (caching)
- Substation (main app - UI coordination)
- Service Layer (business logic)
- SwiftNCurses (terminal UI framework - custom implementation)
Does Substation work on Windows?¶
Not yet. Use WSL2 (Windows Subsystem for Linux) if on Windows.
Why not Windows?
- Windows terminal APIs are fundamentally different (not ncurses)
- Swift on Windows has limited server-side support
- Cross-platform terminal abstraction is complex
Workaround:
# Install WSL2 and Ubuntu
wsl --install
# Inside WSL2
git clone https://github.com/cloudnull/substation.git
cd substation
~/.swiftly/bin/swift build -c release
Why Swift 6.1? Can I use Swift 5.x?¶
No. Swift 6 strict concurrency is required.
Substation enforces a zero-warning build standard with Swift 6 strict concurrency checking. This eliminates:
- Race conditions (compile-time prevention)
- Data races (actor isolation)
- Thread safety bugs (guaranteed by compiler)
Building Requirement:
# Swift 6.1 or later required
~/.swiftly/bin/swift --version
# Must show: Swift version 6.1 or later
What is MemoryKit?¶
MemoryKit is Substation's multi-level caching system.
Components:
MultiLevelCacheManager.swift- L1/L2/L3 cache hierarchyCacheManager.swift- Primary cache engine with TTL managementMemoryManager.swift- Memory pressure detection and cleanupTypedCacheManager.swift- Type-safe cachingPerformanceMonitor.swift- Real-time metrics and alerts
Features:
- L1 (Memory): < 1ms, 80% hit rate
- L2 (Larger Memory): ~5ms, 15% hit rate
- L3 (Disk): ~20ms, 3% hit rate
- Automatic eviction at 85% memory threshold
- Resource-specific TTLs (2 min to 1 hour)
How does actor-based concurrency work in Substation?¶
All shared state is protected by actors (Swift 6 strict concurrency).
Examples:
// Token manager is an actor
public actor CoreTokenManager {
private var encryptedToken: Data? // Protected by actor
public func getValidToken() async throws -> String {
// Automatic serialization by Swift runtime
}
}
// OpenStack client core is an actor
public actor OpenStackClientCore {
private let tokenManager: CoreTokenManager
public func request<T: Decodable>(...) async throws -> T {
let token = try await ensureAuthenticated()
// Thread-safe by design
}
}
UI is MainActor:
Result: Zero race conditions, guaranteed by compiler.
Security Questions¶
How are credentials stored?¶
Substation implements comprehensive security measures for credential protection. For complete details, see the Security Guide.
Quick Summary:
- Credentials from clouds.yaml are read once at startup, never written to disk
- Tokens are encrypted in memory using platform-specific encryption
- Tokens are automatically refreshed before expiration
- All sensitive data is cleared on exit
Best Practice:
Are tokens logged in wiretap mode?¶
No. Wiretap mode redacts all sensitive information. For complete security details, see the Security Guide.
Wiretap logs HTTP methods, URLs, response codes, and timing - but never logs tokens, passwords, or secrets.
How do I report a security vulnerability?¶
Do not file public GitHub issues for security vulnerabilities.
Instead:
- Email security contact (check repository README)
- Include detailed description
- Provide steps to reproduce
- Allow time for patch before public disclosure
Development Questions¶
How do I contribute to Substation?¶
We welcome contributions!
Process:
- Fork the repository
- Create a feature branch
- Make your changes
- Ensure zero warnings:
~/.swiftly/bin/swift buildmust have zero warnings - Add tests if applicable
- Submit a pull request
Code Standards:
- Swift 6.1 strict concurrency
- Zero warnings build requirement
- Actor-based concurrency for shared state
- Never use Unicode (ASCII only)
- Building warnings treated as errors
Why the zero-warning requirement?¶
Warnings become bugs in production.
Substation enforces zero-warning builds to ensure:
- No concurrency issues (data races, race conditions)
- No memory safety issues
- No undefined behavior
- Production-ready code quality
Every warning must be fixed before merge.
Getting Help¶
Where can I find more documentation?¶
- Built-in help: Press
?at any time - Online docs: substation.cloud
- GitHub Wiki: Detailed guides and tutorials
- API Reference: substation.cloud/api
How do I report bugs?¶
Report issues on GitHub:
- Check existing issues first
- Provide reproduction steps
- Include version and configuration
- Attach debug logs if possible
Where can I ask questions?¶
- GitHub Discussions: Community forum
- Stack Overflow: Tag
substation-tui